The Rise of the Textile Industry in Charlotte's History
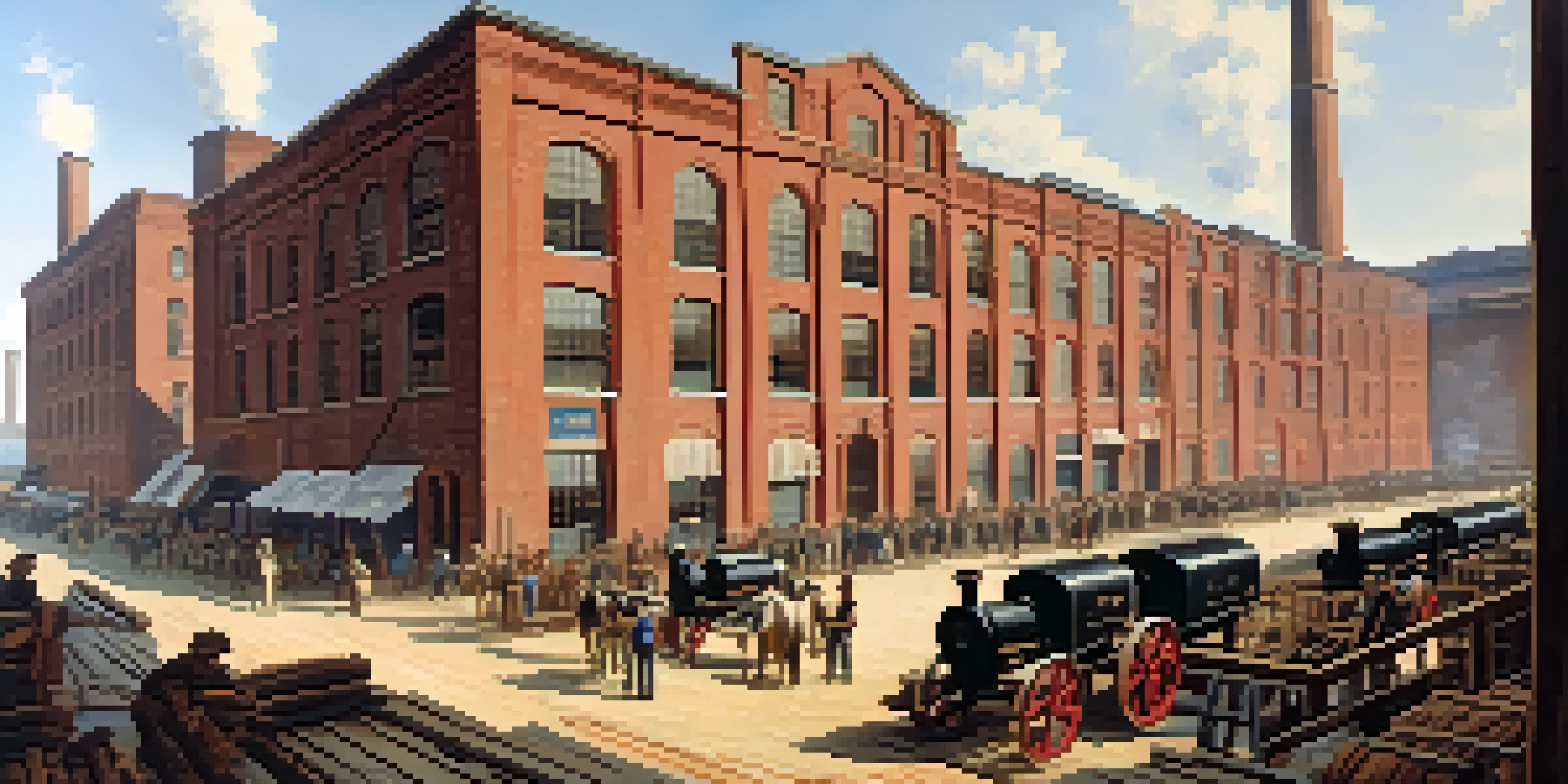

The Early Beginnings of Textile Manufacturing in Charlotte
Charlotte's textile story begins in the late 19th century, fueled by the Industrial Revolution. At this time, the city was primarily an agricultural hub, but the demand for cotton prompted a shift towards manufacturing. Mills began sprouting up, transforming the city from a rural community into an industrial center. This transition laid the foundation for what would become a booming textile industry.
The textile industry is a reflection of the culture, innovation, and resilience of a community.
The establishment of the first cotton mills in the 1880s marked a significant turning point for Charlotte. These mills harnessed the region's abundant cotton supply, allowing local entrepreneurs to capitalize on the growing market. With easy access to transportation routes, both by rail and water, Charlotte was poised to become a textile leader. This era saw the city’s population and economy start to flourish, fueled by the burgeoning textile sector.
As the textile mills expanded, they attracted workers from across the region, creating a diverse labor force. Families migrated to Charlotte in search of employment opportunities, and the city began to develop its unique cultural identity. This influx not only contributed to the economic growth but also fostered a sense of community among those who worked in the textile industry.
The Role of the Cotton Economy in Textile Growth
Cotton was the lifeblood of Charlotte's textile industry, deeply intertwined with the region's economy. The rich soil and favorable climate made North Carolina one of the top cotton-producing states in the country. This abundance meant that local mills had a consistent supply of raw material, which was crucial for their operations. As a result, Charlotte became a central hub for cotton processing and textile production.
The local economy thrived as cotton prices soared in the early 20th century, providing mill owners with significant profits. This financial success encouraged further investment in mill technology and infrastructure. Innovations like the cotton gin and advancements in weaving techniques increased productivity, allowing mills to produce textiles at an unprecedented scale. The synergy between cotton production and textile manufacturing created a dynamic economic environment for Charlotte.
Charlotte's Textile Industry Origins
The late 19th century marked Charlotte's transformation from an agricultural hub to a textile manufacturing center, driven by the demand for cotton.
However, this reliance on cotton also had its drawbacks. Fluctuations in cotton prices and the cyclical nature of agricultural production meant that the textile industry faced challenges. Despite these obstacles, the resilience of Charlotte's textile sector allowed it to adapt and flourish, reinforcing its status as an industrial powerhouse.
The Impact of Railroads on Textile Distribution
The arrival of railroads in the late 1800s revolutionized the textile industry in Charlotte. Rail networks not only facilitated the transportation of raw cotton to mills but also enabled the distribution of finished textile products to markets across the country. This connectivity opened up new business opportunities and helped local manufacturers expand their reach beyond the regional market.
In the midst of change, those who adapt and innovate will not only survive but thrive.
With efficient rail transport, mills could operate at a larger scale, significantly reducing costs and increasing profitability. The ease of transporting goods meant that Charlotte's textiles could compete with those produced in more established industrial cities. This competitive edge attracted even more investment into the local textile sector, fueling its rapid growth and innovation.
Moreover, the railroads played a vital role in fostering relationships with suppliers and retailers. Mill owners could establish partnerships with cotton farmers and textile distributors, creating a network that supported the entire supply chain. This interdependence further solidified Charlotte's position as a significant player in the textile industry.
The Rise of Mill Villages and Community Life
As textile mills flourished, so did the communities that formed around them, known as mill villages. These villages provided housing, schools, and recreational facilities for mill workers and their families. Life in these communities was often tightly knit, with shared experiences and traditions that fostered a strong sense of belonging. The mill village culture contributed significantly to the social fabric of Charlotte during this period.
The mills not only employed workers but also played a crucial role in shaping their lives. Many families spent generations working in the same mills, creating a legacy of labor that defined their identities. Social gatherings, church events, and community celebrations were common, reinforcing relationships among residents. This communal lifestyle offered support during challenging times, reflecting the resilience of the mill workers.
Impact of Railroads on Growth
The arrival of railroads in the late 1800s revolutionized textile distribution, enabling Charlotte's mills to expand their market reach significantly.
However, the reliance on mill work also came with challenges. The long hours, low wages, and demanding conditions often took a toll on workers. Despite these hardships, the sense of community and shared purpose helped individuals navigate the difficulties of mill life, highlighting the complex dynamics of the textile industry's growth in Charlotte.
Technological Advancements Transforming Textile Production
As the textile industry matured, technological advancements played a pivotal role in transforming production methods. Innovations such as the spinning frame and power loom increased efficiency and output, allowing mills to produce textiles at a fraction of the previous cost. These advancements not only enhanced productivity but also improved the quality of the finished products, making Charlotte's textiles more competitive in the market.
The introduction of synthetic fibers in the mid-20th century further revolutionized the industry. Materials like nylon and polyester offered new possibilities for textile manufacturing, enabling mills to diversify their product lines. This adaptability was crucial for Charlotte's textile sector, as it allowed local manufacturers to stay relevant amid changing consumer preferences and market demands.
Furthermore, the push towards automation and computerization in the late 20th century transformed traditional processes. While this shift meant that fewer workers were needed, it also created opportunities for skilled labor in technology and engineering. The evolution of the textile industry in Charlotte illustrates how innovation can drive growth and reshape the landscape of an entire sector.
Challenges Facing the Textile Industry in Charlotte
Despite its successes, Charlotte's textile industry faced numerous challenges, particularly in the latter half of the 20th century. Globalization led to increased competition from overseas manufacturers, where labor costs were significantly lower. This shift prompted many local mills to either downsize or close their doors, leading to a decline in employment opportunities in the textile sector.
Additionally, changing consumer preferences toward fast fashion and cheaper alternatives put further pressure on local manufacturers. As the demand for low-cost textiles surged, many established mills struggled to keep up. This shift not only impacted the economy but also changed the landscape of the textile industry in Charlotte, forcing it to adapt or risk obsolescence.
Legacy of Community and Innovation
Today, the textile industry's legacy in Charlotte is reflected in a renewed focus on sustainable practices and local production, blending tradition with modern innovation.
The decline of the textile industry had profound social implications as well. Many communities that relied on mill jobs faced economic instability, leading to a loss of cultural identity. However, the resilience of Charlotte's residents has led to efforts to revitalize the local economy, focusing on innovation and diversification in other sectors.
The Legacy of the Textile Industry in Charlotte Today
Today, the legacy of the textile industry is still evident in Charlotte, even as the sector has evolved. While many traditional mills have closed, the influence of this industry can be seen in the region's economic development and cultural heritage. The stories of mill workers and their communities continue to shape the identity of Charlotte, reminding residents of their rich industrial past.
In recent years, there has been a resurgence of interest in textiles, particularly in sustainable practices and local production. Entrepreneurs and designers are revisiting traditional methods while integrating modern technology, creating a unique blend of old and new. This movement not only pays homage to Charlotte's textile roots but also fosters innovation and creativity in the industry.
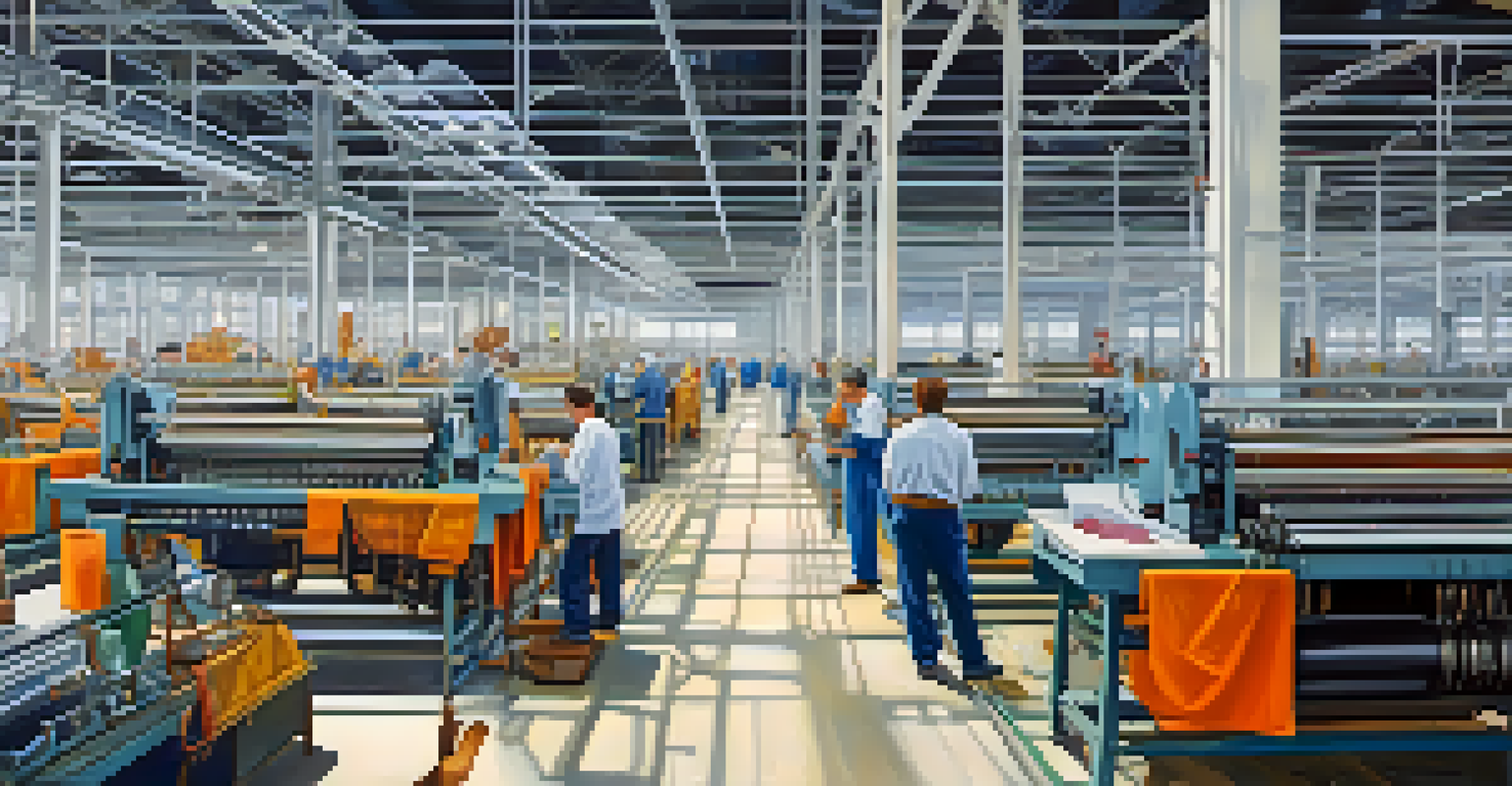

Furthermore, the lessons learned from the rise and decline of the textile industry serve as important reminders for future generations. The ability to adapt to change, embrace innovation, and maintain a strong sense of community will remain crucial as Charlotte continues to grow and evolve in an ever-changing global landscape.